- 5 Dec 2013
- [International Secretariat]
- Region: DEMOCRATIC PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF KOREA
- Topic:
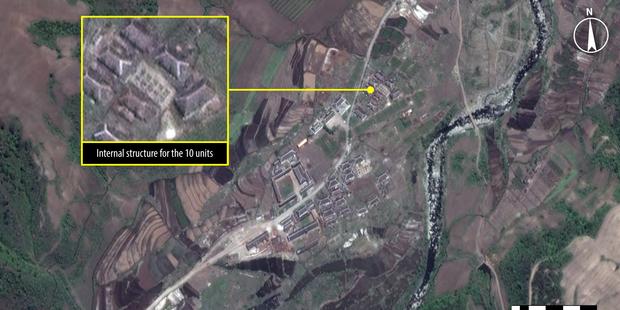
A satellite image from Kwanliso 16, the largest political prison camp in North Korea. (C) Analysis secured by Amnesty International (C) DigitalGlobe 2013
North Korea’s vast infrastructure of repression is further exposed in new satellite images showing the on-going development of two of the country’s largest political prison camps, Amnesty International discloses today. In a comprehensive assessments of camps 15 and 16 - known as kwanliso - Amnesty International found new housing blocks, an expansion of production facilities, and continued tight security.
The analysis, along with newly released testimonies, is included in Amnesty International’s latest briefing North Korea: Continued Investment in the Infrastructure of Repression.
A former security official at kwanliso 16 – the largest political prison camp in North Korea – has never spoken publicly before. He describes detainees being forced to dig their own graves and women being raped and then disappearing.
Amnesty International has shared the latest evidence with the UN Commission of Inquiry investigating human rights abuses in North Korea.
Hundreds of thousands of people--including children--are detained in political prison camps and other detention facilities in North Korea.
Many of those have not committed any crime but are merely family members of those deemed guilty of serious political crimes. They are detained as a form of collective punishment, “guilt-by-association”.
Kwanliso 16, near Hwaseong in North Hamgyong province, is approximately 560 km2, three times the size of the US capital Washington DC. It is one of the least investigated areas in the vast political prison camp system. In 2011, an estimated 20,000 people were believed be imprisoned at kwanliso 16.
The latest images, taken in May 2013, indicate a slight increase in kwanliso 16’s population with new housing blocks clearly visible. The pictures captured housing being built, giving a possible insight into the living conditions detainees face.
Significant economic activity--such as mining, logging and agriculture--is clearly visible in the satellite images. The images show an expansion of an industrial area within kwanliso 16.
Forced hard labour is common in North Korea’s political prison camps. Testimony from former detainees and officials reveals how detainees spend most of their time being forced to work in dangerous conditions with little time to rest.
Security remains tight, with perimeter fences and security points clearly marked. Movement appears to be restricted and controlled through secured entrance gates, guard towers and internal check points.
Mr Lee, a former security official at Camp 16 in the 1980s until the mid 1990s, told Amnesty International in an interview in November 2013 of the methods used to execute prisoners. Detainees were forced to dig their own graves and were then killed with hammer blows to their necks. He also witnessed prison officers strangling detainees and then beating them to death with wooden sticks.
According to Mr Lee women were disappeared after being raped: “After a night of ‘servicing’ the officials, the women had to die because the secret could not get out. This happens at most of the political prison camps.”
Kim Young-soon, a former detainee in Camp 15 between 1980 and 1989, described a public execution she witnessed of two detainees who were caught attempting to escape: “They were brought to a stage after they were badly beaten. The prisoners were tied to wooden stakes and shot three times in their head, chest and feet.”
The recent images of Camp 15--also known as Yodok--show that 39 housing blocks have been demolished since Amnesty International last assessed satellite pictures of the camp in 2011. Only six new housing blocks have been built. The decrease in housing could indicate a slight reduction in the kwanliso population. However, Amnesty International is not able to verify the prisoner population or the fate of the detainees.
Kwanliso 15 covers an area of 370 km2 and is located in central North Korea around 120km from the capital Pyongyang. In 2011, an estimated 50,000 people were imprisoned within the camp and the population is concentrated in river valleys.
Similar to kwanliso 16, security remains tight in Yodok, and there is significant economic activity. For example, logging activities are clearly visible, as is the processing of raw lumber in a likely furniture factory.
5 December 2013
AMNESTY INTERNATIONAL PRESS RELEASE
Related Actions
Related Newses
- 16 Dec 2016 [International Secretariat]
DEMOCRATIC PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF KOREA: North Korea prison camps very much in working order - 9 Mar 2016 [International Secretariat]
DEMOCRATIC PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF KOREA: Tightened controls on communications with the outside world leave families devastated -Restrictions on communications compound North Korea’s dire human rights situation- - 20 Nov 2014 [International Secretariat]
DEMOCRATIC PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF KOREA: UN vote a crucial step to ensure perpetrators of crimes against humanity face justice - 1 Apr 2014 [International Secretariat]
DEMOCRATIC PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF KOREA: North Korea: UN vote a positive step to end crimes against humanity - 18 Feb 2014 [International Secretariat]
DEMOCRATIC PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF KOREA: UN Security Council must act on crimes against humanity




